Neurodiversity in the Workplace: Reshaping Corporate Culture
The concept of neurodiversity is transforming how companies approach talent acquisition and management. This paradigm shift recognizes cognitive differences as natural variations in human neurology rather than deficits. As businesses increasingly embrace neurodiversity, they're discovering untapped potential and innovative perspectives that can drive success in unexpected ways.
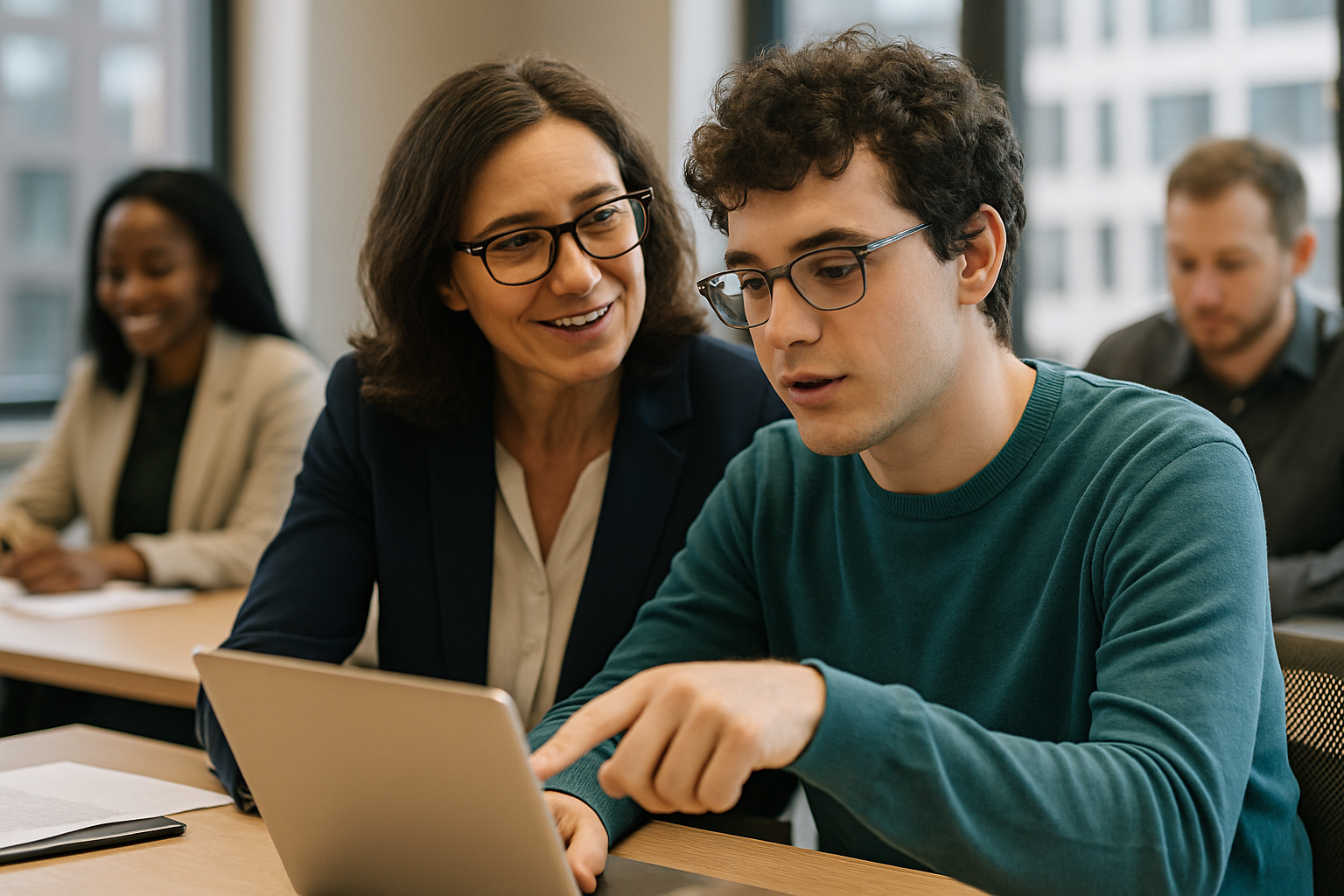

In the workplace context, neurodiversity initiatives aim to create inclusive environments that recognize and leverage the unique strengths of neurodiverse individuals. This approach not only promotes equality but also taps into a wealth of talent that has historically been overlooked or underutilized in corporate settings.
The Business Case for Neurodiversity
Companies embracing neurodiversity are discovering significant benefits. Many neurodiverse individuals possess exceptional skills in pattern recognition, memory, and attention to detail. For instance, some autistic individuals excel in data analysis and quality control tasks, often outperforming their neurotypical peers in these areas.
Tech giants like Microsoft, SAP, and HP have implemented neurodiversity programs, reporting improvements in productivity, quality, and innovation. These companies have found that neurodiverse teams often bring fresh perspectives to problem-solving, leading to creative solutions and increased efficiency.
Moreover, fostering a neurodiverse workforce can enhance a company’s reputation, attracting top talent and resonating with consumers who value inclusive practices. As social responsibility becomes increasingly important to stakeholders, neurodiversity initiatives can contribute to a positive corporate image.
Challenges and Adaptations
Implementing neurodiversity programs isn’t without challenges. Traditional hiring practices, workplace environments, and management styles may inadvertently exclude or disadvantage neurodiverse individuals. Companies must adapt their processes to create truly inclusive spaces.
One key area for adaptation is the recruitment process. Standard interview techniques may not effectively assess the skills of neurodiverse candidates. Some companies have introduced alternative assessment methods, such as work trials or skill-based tests, which provide a more accurate picture of a candidate’s abilities.
Workplace design is another crucial consideration. Open-plan offices, common in many corporations, can be overwhelming for some neurodiverse individuals. Companies are experimenting with flexible spaces, quiet zones, and sensory-friendly areas to accommodate diverse needs.
Training and Support
Educating neurotypical employees and managers about neurodiversity is essential for creating an inclusive culture. Many companies are implementing training programs to raise awareness, combat stereotypes, and provide strategies for effective communication and collaboration with neurodiverse colleagues.
Support systems are also crucial. Some organizations have introduced mentorship programs or dedicated support staff to help neurodiverse employees navigate workplace challenges. These resources can be invaluable in ensuring long-term success and retention of neurodiverse talent.
The Ripple Effect
The impact of neurodiversity initiatives extends beyond the workplace. As more companies embrace cognitive differences, it’s influencing broader societal attitudes towards neurodiversity. This shift is challenging long-held assumptions about intelligence, productivity, and the nature of work itself.
Moreover, the success of neurodiversity programs in the corporate world is inspiring changes in education and public policy. Schools are beginning to adopt more inclusive approaches to learning, while policymakers are considering how to better support neurodiverse individuals in various aspects of life.
Future Directions
As neurodiversity becomes more mainstream in corporate culture, we can expect to see further innovations in workplace practices and technologies. Artificial intelligence and machine learning may play a role in creating more personalized work environments that adapt to individual cognitive styles.
The concept of neurodiversity may also expand to encompass a wider range of cognitive variations, leading to even more inclusive and diverse workplaces. This evolution could challenge traditional notions of career paths and success, opening up new possibilities for individuals with diverse cognitive profiles.
In conclusion, the integration of neurodiversity into corporate culture represents a significant shift in how we understand and value human differences. By recognizing and harnessing the strengths of neurodiverse individuals, companies are not only creating more inclusive workplaces but also driving innovation and success in an increasingly complex global economy. As this trend continues to grow, it has the potential to reshape not just corporate landscapes, but societal attitudes towards cognitive diversity as a whole.